Command Line Interface
spaCy’s CLI provides a range of helpful commands for downloading and training
pipelines, converting data and debugging your config, data and installation. For
a list of available commands, you can type python -m spacy --help. You can
also add the --help flag to any command or subcommand to see the description,
available arguments and usage.
download command
Download trained pipelines for spaCy. The downloader finds the
best-matching compatible version and uses pip install to download the Python
package. Direct downloads don’t perform any compatibility checks and require the
pipeline name to be specified with its version (e.g. en_core_web_sm-3.0.0).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
model | Pipeline package name, e.g. en_core_web_sm. str |
--direct, -D | Force direct download of exact package version. bool |
--sdist, -S v3.0 | Download the source package (.tar.gz archive) instead of the default pre-built binary wheel. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| pip args | Additional installation options to be passed to pip install when installing the pipeline package. For example, --user to install to the user home directory or --no-deps to not install package dependencies. Any |
| CREATES | The installed pipeline package in your site-packages directory. |
info command
Print information about your spaCy installation, trained pipelines and local setup, and generate Markdown-formatted markup to copy-paste into GitHub issues.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
model | A trained pipeline, i.e. package name or path (optional). Optional[str] |
--markdown, -md | Print information as Markdown. bool |
--silent, -s | Don’t print anything, just return the values. bool |
--exclude, -e | Comma-separated keys to exclude from the print-out. Defaults to "labels". Optional[str] |
--url, -u v3.5.0 | Print the URL to download the most recent compatible version of the pipeline. Requires a pipeline name. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| PRINTS | Information about your spaCy installation. |
validate command
Find all trained pipeline packages installed in the current environment and
check whether they are compatible with the currently installed version of spaCy.
Should be run after upgrading spaCy via pip install -U spacy to ensure that
all installed packages can be used with the new version. It will show a list of
packages and their installed versions. If any package is out of date, the latest
compatible versions and command for updating are shown.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PRINTS | Details about the compatibility of your installed pipeline packages. |
init v3.0
The spacy init CLI includes helpful commands for initializing training config
files and pipeline directories.
init config commandv3.0
Initialize and save a config.cfg file using the
recommended settings for your use case. It works just like the
quickstart widget, only that it also auto-fills
all default values and exports a training-ready
config. The settings you specify will impact the suggested model architectures
and pipeline setup, as well as the hyperparameters. You can also adjust and
customize those settings in your config file later.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
output_file | Path to output .cfg file or - to write the config to stdout (so you can pipe it forward to a file or to the train command). Note that if you’re writing to stdout, no additional logging info is printed. Path |
--lang, -l | Optional code of the language to use. Defaults to "en". str |
--pipeline, -p | Comma-separated list of trainable pipeline components to include. Defaults to "tagger,parser,ner". str |
--optimize, -o | "efficiency" or "accuracy". Whether to optimize for efficiency (faster inference, smaller model, lower memory consumption) or higher accuracy (potentially larger and slower model). This will impact the choice of architecture, pretrained weights and related hyperparameters. Defaults to "efficiency". str |
--gpu, -G | Whether the model can run on GPU. This will impact the choice of architecture, pretrained weights and related hyperparameters. bool |
--pretraining, -pt | Include config for pretraining (with spacy pretrain). Defaults to False. bool |
--force, -f | Force overwriting the output file if it already exists. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | The config file for training. |
init fill-config v3.0
Auto-fill a partial .cfg file with all default values, e.g. a config generated with the quickstart widget. Config files used for training should always be complete and not contain any hidden defaults or missing values, so this command helps you create your final training config. In order to find the available settings and defaults, all functions referenced in the config will be created, and their signatures are used to find the defaults. If your config contains a problem that can’t be resolved automatically, spaCy will show you a validation error with more details.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
base_path | Path to base config to fill, e.g. generated by the quickstart widget. Path |
output_file | Path to output .cfg file or ”-” to write to stdout so you can pipe it to a file. Defaults to ”-” (stdout). Path |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--pretraining, -pt | Include config for pretraining (with spacy pretrain). Defaults to False. bool |
--diff, -D | Print a visual diff highlighting the changes. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | Complete and auto-filled config file for training. |
init fill-curated-transformer commandv3.7
Auto-fill the Hugging Face model hyperpameters and loader parameters of a
Curated Transformer pipeline component in a
.cfg file. The name and revision of the
Hugging Face model can either be passed as
command-line arguments or read from the
initialize.components.transformer.encoder_loader config section.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
base_path | Path to base config to fill, e.g. generated by the quickstart widget. Path |
output_file | Path to output .cfg file or ”-” to write to stdout so you can pipe it to a file. Defaults to ”-” (stdout). Path |
--model-name, -m | Name of the Hugging Face model. Defaults to the model name from the encoder loader config. Optional[str] |
--model-revision, -r | Revision of the Hugging Face model. Defaults to main. Optional[str] |
--pipe-name, -n | Name of the Curated Transformer pipe whose config is to be filled. Defaults to the first transformer pipe. Optional[str] |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
| CREATES | Complete and auto-filled config file for training. |
init vectors commandv3.0
Convert word vectors for use
with spaCy. Will export an nlp object that you can use in the
[initialize] block of your config to
initialize a model with vectors. See the usage guide on
static vectors for details on
how to use vectors in your model.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
lang | Pipeline language IETF language tag, such as en. str |
vectors_loc | Location of vectors. Should be a file where the first row contains the dimensions of the vectors, followed by a space-separated Word2Vec table. File can be provided in .txt format or as a zipped text file in .zip or .tar.gz format. Path |
output_dir | Pipeline output directory. Will be created if it doesn’t exist. Path |
--truncate, -t | Number of vectors to truncate to when reading in vectors file. Defaults to 0 for no truncation. int |
--prune, -p | Number of vectors to prune the vocabulary to. Defaults to -1 for no pruning. int |
--mode, -m | Vectors mode: default or floret. Defaults to default. str |
--attr, -a | Token attribute to use for vectors, e.g. LOWER or NORM) Defaults to ORTH. str |
--name, -n | Name to assign to the word vectors in the meta.json, e.g. en_core_web_md.vectors. Optional[str] |
--verbose, -V | Print additional information and explanations. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | A spaCy pipeline directory containing the vocab and vectors. |
init labels commandv3.0
Generate JSON files for the labels in the data. This helps speed up the training
process, since spaCy won’t have to preprocess the data to extract the labels.
After generating the labels, you can provide them to components that accept a
labels argument on initialization via the
[initialize] block of your config.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to training config file containing all settings and hyperparameters. If -, the data will be read from stdin. Union[Path, str] |
output_path | Output directory for the label files. Will create one JSON file per component. Path |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--verbose, -V | Show more detailed messages for debugging purposes. bool |
--gpu-id, -g | GPU ID or -1 for CPU. Defaults to -1. int |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| overrides | Config parameters to override. Should be options starting with -- that correspond to the config section and value to override, e.g. --paths.train ./train.spacy. Any |
| CREATES | The label files. |
find-function commandv3.7
Find the module, path and line number to the file for a given registered function. This functionality is helpful to understand where registered functions, as used in the config file, are defined.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
func_name | Name of the registered function. str |
--registry, -r | Name of the catalogue registry. str |
convert command
Convert files into spaCy’s
binary training data format, a serialized
DocBin, for use with the train command and other experiment
management functions. The converter can be specified on the command line, or
chosen based on the file extension of the input file.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
input_path | Input file or directory. Path |
output_dir | Output directory for converted file. Defaults to "-", meaning data will be written to stdout. Optional[Path] |
--converter, -c | Name of converter to use (see below). str |
--file-type, -t | Type of file to create. Either spacy (default) for binary DocBin data or json for v2.x JSON format. str |
--n-sents, -n | Number of sentences per document. Supported for: conll, conllu, iob, ner int |
--seg-sents, -s | Segment sentences. Supported for: conll, ner bool |
--base, -b, --model | Trained spaCy pipeline for sentence segmentation to use as base (for --seg-sents). Optional[str] |
--morphology, -m | Enable appending morphology to tags. Supported for: conllu bool |
--merge-subtokens, -T | Merge CoNLL-U subtokens bool |
--ner-map, -nm | NER tag mapping (as JSON-encoded dict of entity types). Supported for: conllu Optional[Path] |
--lang, -l | Language code (if tokenizer required). Optional[str] |
--concatenate, -C | Concatenate output to a single file bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | Binary DocBin training data that can be used with spacy train. |
Converters
| ID | Description |
|---|---|
auto | Automatically pick converter based on file extension and file content (default). |
json | JSON-formatted training data used in spaCy v2.x. |
conllu | Universal Dependencies .conllu format. |
ner / conll | NER with IOB/IOB2/BILUO tags, one token per line with columns separated by whitespace. The first column is the token and the final column is the NER tag. Sentences are separated by blank lines and documents are separated by the line -DOCSTART- -X- O O. Supports CoNLL 2003 NER format. See sample data. |
iob | NER with IOB/IOB2/BILUO tags, one sentence per line with tokens separated by whitespace and annotation separated by |, either word|B-ENTorword|POS|B-ENT. See sample data. |
debug v3.0
The spacy debug CLI includes helpful commands for debugging and profiling your
configs, data and implementations.
debug config commandv3.0
Debug a config.cfg file and show validation errors.
The command will create all objects in the tree and validate them. Note that
some config validation errors are blocking and will prevent the rest of the
config from being resolved. This means that you may not see all validation
errors at once and some issues are only shown once previous errors have been
fixed. To auto-fill a partial config and save the result, you can use the
init fill-config command.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to training config file containing all settings and hyperparameters. If -, the data will be read from stdin. Union[Path, str] |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--show-functions, -F | Show an overview of all registered function blocks used in the config and where those functions come from, including the module name, Python file and line number. bool |
--show-variables, -V | Show an overview of all variables referenced in the config, e.g. ${paths.train} and their values that will be used. This also reflects any config overrides provided on the CLI, e.g. --paths.train /path. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| overrides | Config parameters to override. Should be options starting with -- that correspond to the config section and value to override, e.g. --paths.train ./train.spacy. Any |
| PRINTS | Config validation errors, if available. |
debug data command
Analyze, debug and validate your training and development data. Get useful stats, and find problems like invalid entity annotations, cyclic dependencies, low data labels and more.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to training config file containing all settings and hyperparameters. If -, the data will be read from stdin. Union[Path, str] |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--ignore-warnings, -IW | Ignore warnings, only show stats and errors. bool |
--verbose, -V | Print additional information and explanations. bool |
--no-format, -NF | Don’t pretty-print the results. Use this if you want to write to a file. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| overrides | Config parameters to override. Should be options starting with -- that correspond to the config section and value to override, e.g. --paths.train ./train.spacy. Any |
| PRINTS | Debugging information. |
debug diff-config command
Show a diff of a config file with respect to spaCy’s defaults or another config file. If additional settings were used in the creation of the config file, then you must supply these as extra parameters to the command when comparing to the default settings. The generated diff can also be used when posting to the discussion forum to provide more information for the maintainers.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to training config file containing all settings and hyperparameters. Union[Path, str] |
compare_to | Path to another config file to diff against, or None to compare against default settings. Optional[Union[Path, str] |
optimize, -o | "efficiency" or "accuracy". Whether the config was optimized for efficiency (faster inference, smaller model, lower memory consumption) or higher accuracy (potentially larger and slower model). Only relevant when comparing against a default config. Defaults to "efficiency". str |
gpu, -G | Whether the config was made to run on a GPU. Only relevant when comparing against a default config. bool |
pretraining, -pt | Include config for pretraining (with spacy pretrain). Only relevant when comparing against a default config. Defaults to False. bool |
markdown, -md | Generate Markdown for Github issues. Defaults to False. bool |
| PRINTS | Diff between the two config files. |
debug profile command
Profile which functions take the most time in a spaCy pipeline. Input should be
formatted as one JSON object per line with a key "text". It can either be
provided as a JSONL file, or be read from sys.sytdin. If no input file is
specified, the IMDB dataset is loaded via
ml_datasets.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
model | A loadable spaCy pipeline (package name or path). str |
inputs | Path to input file, or - for standard input. Path |
--n-texts, -n | Maximum number of texts to use if available. Defaults to 10000. int |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| PRINTS | Profiling information for the pipeline. |
debug model commandv3.0
Debug a Thinc Model by running it on a
sample text and checking how it updates its internal weights and parameters.
In this example log, we just print the name of each layer after creation of the model (“Step 0”), which helps us to understand the internal structure of the Neural Network, and to focus on specific layers that we want to inspect further (see next example).
In this example log, we see how initialization of the model (Step 1) propagates
the correct values for the nI (input) and nO (output) dimensions of the
various layers. In the softmax layer, this step also defines the W matrix as
an all-zero matrix determined by the nO and nI dimensions. After a first
training step (Step 2), this matrix has clearly updated its values through the
training feedback loop.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to training config file containing all settings and hyperparameters. If -, the data will be read from stdin. Union[Path, str] |
component | Name of the pipeline component of which the model should be analyzed. str |
--layers, -l | Comma-separated names of layer IDs to print. str |
--dimensions, -DIM | Show dimensions of each layer. bool |
--parameters, -PAR | Show parameters of each layer. bool |
--gradients, -GRAD | Show gradients of each layer. bool |
--attributes, -ATTR | Show attributes of each layer. bool |
--print-step0, -P0 | Print model before training. bool |
--print-step1, -P1 | Print model after initialization. bool |
--print-step2, -P2 | Print model after training. bool |
--print-step3, -P3 | Print final predictions. bool |
--gpu-id, -g | GPU ID or -1 for CPU. Defaults to -1. int |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| overrides | Config parameters to override. Should be options starting with -- that correspond to the config section and value to override, e.g. --paths.train ./train.spacy. Any |
| PRINTS | Debugging information. |
debug pieces commandv3.7
Analyze word- or sentencepiece stats.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to config file. Union[Path, str] |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--name, -n | Name of the Curated Transformer pipe whose config is to be filled. Defaults to the first transformer pipe. Optional[str] |
| overrides | Config parameters to override. Should be options starting with -- that correspond to the config section and value to override, e.g. --paths.train ./train.spacy. Any |
| PRINTS | Debugging information. |
train command
Train a pipeline. Expects data in spaCy’s
binary format and a
config file with all settings and hyperparameters.
Will save out the best model from all epochs, as well as the final pipeline. The
--code argument can be used to provide a Python file that’s imported before
the training process starts. This lets you register
custom functions and architectures and refer
to them in your config, all while still using spaCy’s built-in train workflow.
If you need to manage complex multi-step training workflows, check out the new
spaCy projects.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to training config file containing all settings and hyperparameters. If -, the data will be read from stdin. Union[Path, str] |
--output, -o | Directory to store trained pipeline in. Will be created if it doesn’t exist. Optional[Path] |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--verbose, -V | Show more detailed messages during training. bool |
--gpu-id, -g | GPU ID or -1 for CPU. Defaults to -1. int |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| overrides | Config parameters to override. Should be options starting with -- that correspond to the config section and value to override, e.g. --paths.train ./train.spacy. Any |
| CREATES | The final trained pipeline and the best trained pipeline. |
Calling the training function from Python v3.2
The training CLI exposes a train helper function that lets you run the
training just like spacy train. Usually it’s easier to use the command line
directly, but if you need to kick off training from code this is how to do it.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to the config to use for training. Union[str,Path] |
output_path | Optional name of directory to save output model in. If not provided a model will not be saved. Optional[Union[str,Path]] |
| keyword-only | |
use_gpu | Which GPU to use. Defaults to -1 for no GPU. int |
overrides | Values to override config settings. Dict[str, Any] |
pretrain commandexperimental
Pretrain the “token to vector” (Tok2vec) layer of pipeline
components on raw text, using an approximate language-modeling objective.
Specifically, we load pretrained vectors, and train a component like a CNN,
BiLSTM, etc to predict vectors which match the pretrained ones. The weights are
saved to a directory after each epoch. You can then include a path to one of
these pretrained weights files in your
training config as the init_tok2vec setting when you
train your pipeline. This technique may be especially helpful if you have little
labelled data. See the usage docs on
pretraining for more info. To read
the raw text, a JsonlCorpus is typically used.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to training config file containing all settings and hyperparameters. If -, the data will be read from stdin. Union[Path, str] |
output_dir | Directory to save binary weights to on each epoch. Path |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--resume-path, -r | Path to pretrained weights from which to resume pretraining. Optional[Path] |
--epoch-resume, -er | The epoch to resume counting from when using --resume-path. Prevents unintended overwriting of existing weight files. Optional[int] |
--gpu-id, -g | GPU ID or -1 for CPU. Defaults to -1. int |
--skip-last, -L v3.5.2 | Skip saving model-last.bin. Defaults to False. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| overrides | Config parameters to override. Should be options starting with -- that correspond to the config section and value to override, e.g. --training.dropout 0.2. Any |
| CREATES | The pretrained weights that can be used to initialize spacy train. |
evaluate command
The evaluate subcommand is superseded by
spacy benchmark accuracy. evaluate is provided as an
alias to benchmark accuracy for compatibility.
benchmark v3.5
The spacy benchmark CLI includes commands for benchmarking the accuracy and
speed of your spaCy pipelines.
accuracy commandv3.5
Evaluate the accuracy of a trained pipeline. Expects a loadable spaCy pipeline
(package name or path) and evaluation data in the
binary .spacy format. The
--gold-preproc option sets up the evaluation examples with gold-standard
sentences and tokens for the predictions. Gold preprocessing helps the
annotations align to the tokenization, and may result in sequences of more
consistent length. However, it may reduce runtime accuracy due to train/test
skew. To render a sample of dependency parses in a HTML file using the
displaCy visualizations, set as output directory as the
--displacy-path argument.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
model | Pipeline to evaluate. Can be a package or a path to a data directory. str |
data_path | Location of evaluation data in spaCy’s binary format. Path |
--output, -o | Output JSON file for metrics. If not set, no metrics will be exported. Optional[Path] |
--code, -c v3.0 | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--gold-preproc, -G | Use gold preprocessing. bool |
--gpu-id, -g | GPU to use, if any. Defaults to -1 for CPU. int |
--displacy-path, -dp | Directory to output rendered parses as HTML. If not set, no visualizations will be generated. Optional[Path] |
--displacy-limit, -dl | Number of parses to generate per file. Defaults to 25. Keep in mind that a significantly higher number might cause the .html files to render slowly. int |
--per-component, -P v3.6 | Whether to return the scores keyed by component name. Defaults to False. bool |
--spans-key, -sk v3.6.2 | Spans key to use when evaluating Doc.spans. Defaults to sc. str |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | Training results and optional metrics and visualizations. |
speed commandv3.5
Benchmark the speed of a trained pipeline with a 95% confidence interval.
Expects a loadable spaCy pipeline (package name or path) and benchmark data in
the binary .spacy format. The pipeline is
warmed up before any measurements are taken.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
model | Pipeline to benchmark the speed of. Can be a package or a path to a data directory. str |
data_path | Location of benchmark data in spaCy’s binary format. Path |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--batch-size, -b | Set the batch size. If not set, the pipeline’s batch size is used. Optional[int] |
--no-shuffle | Do not shuffle documents in the benchmark data. bool |
--gpu-id, -g | GPU to use, if any. Defaults to -1 for CPU. int |
--batches | Number of batches to benchmark on. Defaults to 50. Optional[int] |
--warmup, -w | Iterations over the benchmark data for warmup. Defaults to 3 Optional[int] |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| PRINTS | Pipeline speed in words per second with a 95% confidence interval. |
apply commandv3.5
Applies a trained pipeline to data and stores the resulting annotated documents
in a DocBin. The input can be a single file or a directory. The recognized
input formats are:
.spacy.jsonlcontaining a user specifiedtext_key- Files with any other extension are assumed to be plain text files containing a single document.
When a directory is provided it is traversed recursively to collect all files.
When loading a .spacy file, any potential annotations stored on the Doc that are not overwritten by the pipeline will be preserved.
If you want to evaluate the pipeline on raw text only, make sure that the .spacy file does not contain any annotations.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
model | Pipeline to apply to the data. Can be a package or a path to a data directory. str |
data_path | Location of data to be evaluated in spaCy’s binary format, jsonl, or plain text. Path |
output-file | Output DocBin path. str |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--text-key, -tk | The key for .jsonl files to use to grab the texts from. Defaults to text. Optional[str] |
--force-overwrite, -F | If the provided output-file already exists, then force apply to overwrite it. If this is False (default) then quits with a warning instead. bool |
--gpu-id, -g | GPU to use, if any. Defaults to -1 for CPU. int |
--batch-size, -b | Batch size to use for prediction. Defaults to 1. int |
--n-process, -n | Number of processes to use for prediction. Defaults to 1. int |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | A DocBin with the annotations from the model for all the files found in data-path. |
find-threshold commandv3.5
Runs prediction trials for a trained model with varying thresholds to maximize
the specified metric. The search space for the threshold is traversed linearly
from 0 to 1 in n_trials steps. Results are displayed in a table on stdout
(the corresponding API call to spacy.cli.find_threshold.find_threshold()
returns all results).
This is applicable only for components whose predictions are influenced by
thresholds - e.g. textcat_multilabel and spancat, but not textcat. Note
that the full path to the corresponding threshold attribute in the config has to
be provided.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
model | Pipeline to evaluate. Can be a package or a path to a data directory. str |
data_path | Path to file with DocBin with docs to use for threshold search. Path |
pipe_name | Name of pipe to examine thresholds for. str |
threshold_key | Key of threshold attribute in component’s configuration. str |
scores_key | Name of score to metric to optimize. str |
--n_trials, -n | Number of trials to determine optimal thresholds. int |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions for new architectures. Optional[Path] |
--gpu-id, -g | GPU to use, if any. Defaults to -1 for CPU. int |
--gold-preproc, -G | Use gold preprocessing. bool |
--verbose, -V, -VV | Display more information for debugging purposes. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
assemble command
Assemble a pipeline from a config file without additional training. Expects a
config file with all settings and hyperparameters.
The --code argument can be used to import a Python file that lets you register
custom functions and refer to them in your
config.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config_path | Path to the config file containing all settings and hyperparameters. If -, the data will be read from stdin. Union[Path, str] |
output_dir | Directory to store the final pipeline in. Will be created if it doesn’t exist. Optional[Path] |
--code, -c | Path to Python file with additional code to be imported. Allows registering custom functions. Optional[Path] |
--verbose, -V | Show more detailed messages during processing. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| overrides | Config parameters to override. Should be options starting with -- that correspond to the config section and value to override, e.g. --paths.data ./data. Any |
| CREATES | The final assembled pipeline. |
package command
Generate an installable Python package from
an existing pipeline data directory. All data files are copied over. If
additional code files are provided (e.g. Python files containing custom
registered functions like
pipeline components), they are
copied into the package and imported in the __init__.py. If the path to a
meta.json is supplied, or a meta.json is found in
the input directory, this file is used. Otherwise, the data can be entered
directly from the command line. spaCy will then create a build artifact that you
can distribute and install with pip install. As of v3.1, the package command
will also create a formatted README.md based on the pipeline information
defined in the meta.json. If a README.md is already present in the source
directory, it will be used instead.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
input_dir | Path to directory containing pipeline data. Path |
output_dir | Directory to create package folder in. Path |
--code, -c v3.0 | Comma-separated paths to Python files to be included in the package and imported in its __init__.py. This allows including registering functions and custom components. str |
--meta-path, -m | Path to meta.json file (optional). Optional[Path] |
--create-meta, -C | Create a meta.json file on the command line, even if one already exists in the directory. If an existing file is found, its entries will be shown as the defaults in the command line prompt. bool |
--build, -b v3.0 | Comma-separated artifact formats to build. Can be sdist (for a .tar.gz archive) and/or wheel (for a binary .whl file), or none if you want to run this step manually. The generated artifacts can be installed by pip install. Defaults to sdist. str |
--name, -n v3.0 | Package name to override in meta. Optional[str] |
--version, -v v3.0 | Package version to override in meta. Useful when training new versions, as it doesn’t require editing the meta template. Optional[str] |
--force, -f | Force overwriting of existing folder in output directory. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | A Python package containing the spaCy pipeline. |
project v3.0
The spacy project CLI includes subcommands for working with
spaCy projects, end-to-end workflows for building and
deploying custom spaCy pipelines.
project clone command
Clone a project template from a Git repository. Calls into git under the hood
and can use the sparse checkout feature if available, so you’re only downloading
what you need. By default, spaCy’s
project templates repo is used, but you
can provide any other repo (public or private) that you have access to using the
--repo option.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
name | The name of the template to clone, relative to the repo. Can be a top-level directory or a subdirectory like dir/template. str |
dest | Where to clone the project. Defaults to current working directory. Path |
--repo, -r | The repository to clone from. Can be any public or private Git repo you have access to. str |
--branch, -b | The branch to clone from. Defaults to master. str |
--sparse, -S | Enable sparse checkout to only check out and download what’s needed. Requires Git v22.2+. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | The cloned project directory. |
project assets command
Fetch project assets like datasets and pretrained weights. Assets are defined in
the assets section of the project.yml. If a
checksum is provided, the file is only downloaded if no local file with the
same checksum exists and spaCy will show an error if the checksum of the
downloaded file doesn’t match. If assets don’t specify a url they’re
considered “private” and you have to take care of putting them into the
destination directory yourself. If a local path is provided, the asset is copied
into the current project.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
project_dir | Path to project directory. Defaults to current working directory. Path |
--extra, -e v3.3.1 | Download assets marked as “extra”. Default false. bool |
--sparse, -S | Enable sparse checkout to only check out and download what’s needed. Requires Git v22.2+. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | Downloaded or copied assets defined in the project.yml. |
project run command
Run a named command or workflow defined in the
project.yml. If a workflow name is specified,
all commands in the workflow are run, in order. If commands define
dependencies or outputs, they will only be
re-run if state has changed. For example, if the input dataset changes, a
preprocessing command that depends on those files will be re-run.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
subcommand | Name of the command or workflow to run. str |
project_dir | Path to project directory. Defaults to current working directory. Path |
--force, -F | Force re-running steps, even if nothing changed. bool |
--dry, -D | Perform a dry run and don’t execute scripts. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| EXECUTES | The command defined in the project.yml. |
project push command
Upload all available files or directories listed as in the outputs section of
commands to a remote storage. Outputs are archived and compressed prior to
upload, and addressed in the remote storage using the output’s relative path
(URL encoded), a hash of its command string and dependencies, and a hash of its
file contents. This means push should never overwrite a file in your
remote. If all the hashes match, the contents are the same and nothing happens.
If the contents are different, the new version of the file is uploaded. Deleting
obsolete files is left up to you.
Remotes can be defined in the remotes section of the
project.yml. Under the hood, spaCy uses
cloudpathlib to communicate with the
remote storages, so you can use any protocol that cloudpathlib supports,
including S3,
Google Cloud Storage, and the local
filesystem, although you may need to install extra dependencies to use certain
protocols.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
remote | The name of the remote to upload to. Defaults to "default". str |
project_dir | Path to project directory. Defaults to current working directory. Path |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| UPLOADS | All project outputs that exist and are not already stored in the remote. |
project pull command
Download all files or directories listed as outputs for commands, unless they
are already present locally. When searching for files in the remote, pull
won’t just look at the output path, but will also consider the command
string and the hashes of the dependencies. For instance, let’s say you’ve
previously pushed a checkpoint to the remote, but now you’ve changed some
hyper-parameters. Because you’ve changed the inputs to the command, if you run
pull, you won’t retrieve the stale result. If you train your pipeline and push
the outputs to the remote, the outputs will be saved alongside the prior
outputs, so if you change the config back, you’ll be able to fetch back the
result.
Remotes can be defined in the remotes section of the
project.yml. Under the hood, spaCy uses
Pathy to communicate with the
remote storages, so you can use any protocol that Pathy supports, including
S3,
Google Cloud Storage, and the local
filesystem, although you may need to install extra dependencies to use certain
protocols.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
remote | The name of the remote to download from. Defaults to "default". str |
project_dir | Path to project directory. Defaults to current working directory. Path |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| DOWNLOADS | All project outputs that do not exist locally and can be found in the remote. |
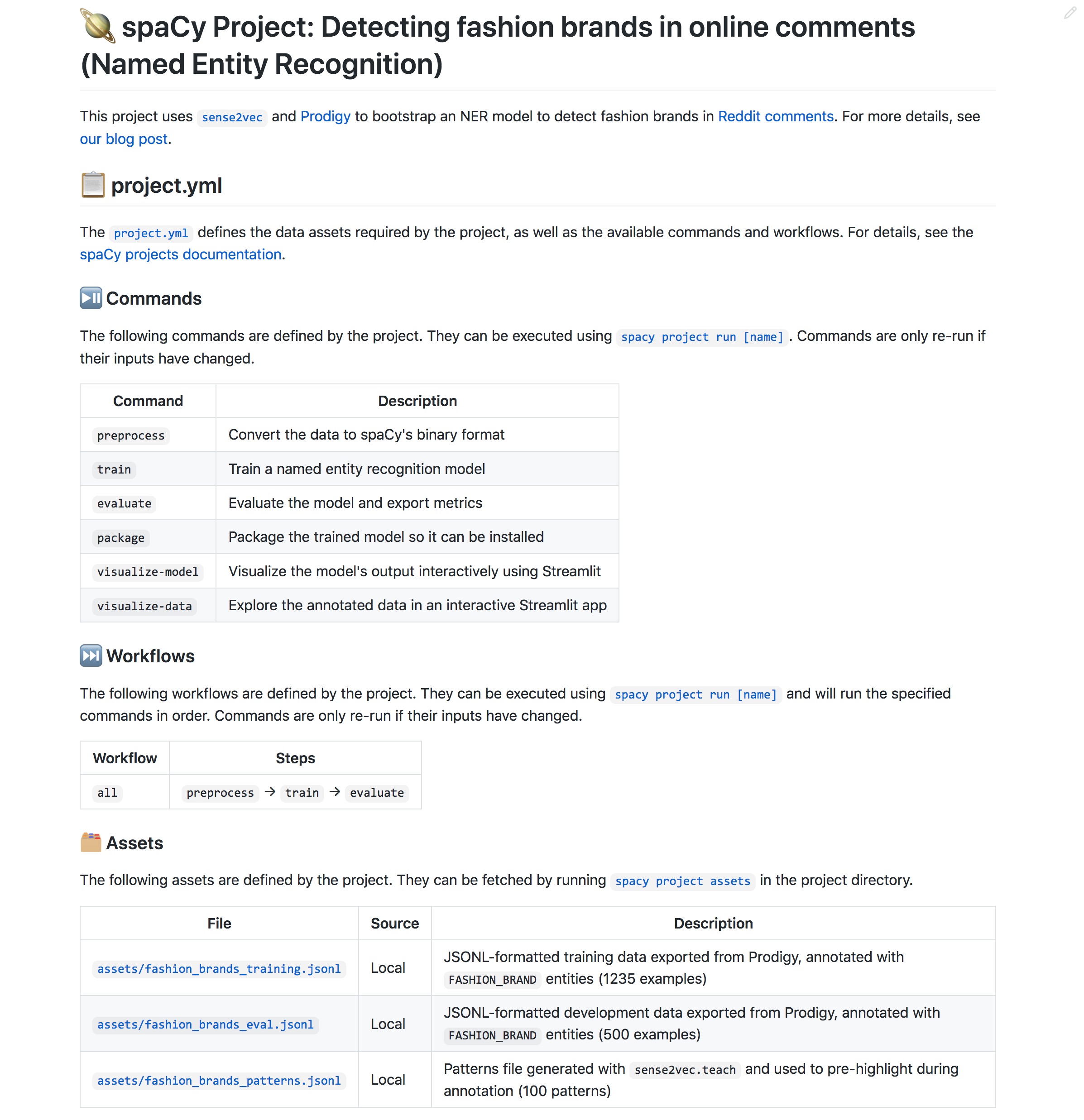
project document command
Auto-generate a pretty Markdown-formatted README for your project, based on
its project.yml. Will create sections that
document the available commands, workflows and assets. The auto-generated
content will be placed between two hidden markers, so you can add your own
custom content before or after the auto-generated documentation. When you re-run
the project document command, only the auto-generated part is replaced.
For more examples, see the templates in our
projects repo.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
project_dir | Path to project directory. Defaults to current working directory. Path |
--output, -o | Path to output file or - for stdout (default). If a file is specified and it already exists and contains auto-generated docs, only the auto-generated docs section is replaced. Path |
--no-emoji, -NE | Don’t use emoji in the titles. bool |
| CREATES | The Markdown-formatted project documentation. |
project dvc command
Auto-generate Data Version Control (DVC) config file. Calls
dvc run with --no-exec under
the hood to generate the dvc.yaml. A DVC project can only define one pipeline,
so you need to specify one workflow defined in the
project.yml. If no workflow is specified, the
first defined workflow is used. The DVC config will only be updated if the
project.yml changed. For details, see the
DVC integration docs.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
project_dir | Path to project directory. Defaults to current working directory. Path |
workflow | Name of workflow defined in project.yml. Defaults to first workflow if not set. Optional[str] |
--force, -F | Force-updating config file. bool |
--verbose, -V | Print more output generated by DVC. bool |
--quiet, -q | Print no output generated by DVC. bool |
--help, -h | Show help message and available arguments. bool |
| CREATES | A dvc.yaml file in the project directory, based on the steps defined in the given workflow. |
huggingface-hub v3.1
The spacy huggingface-cli CLI includes commands for uploading your trained
spaCy pipelines to the Hugging Face Hub.
huggingface-hub push command
Push a spaCy pipeline to the Hugging Face Hub. Expects a .whl file packaged
with spacy package and --build wheel. For more details,
see the spaCy project integration.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
whl_path | The path to the .whl file packaged with spacy package. Path(positional) |
--org, -o | Optional name of organization to which the pipeline should be uploaded. str |
--msg, -m | Commit message to use for update. Defaults to "Update spaCy pipeline". str |
--verbose, -V | Output additional info for debugging, e.g. the full generated hub metadata. bool |
| UPLOADS | The pipeline to the hub. |