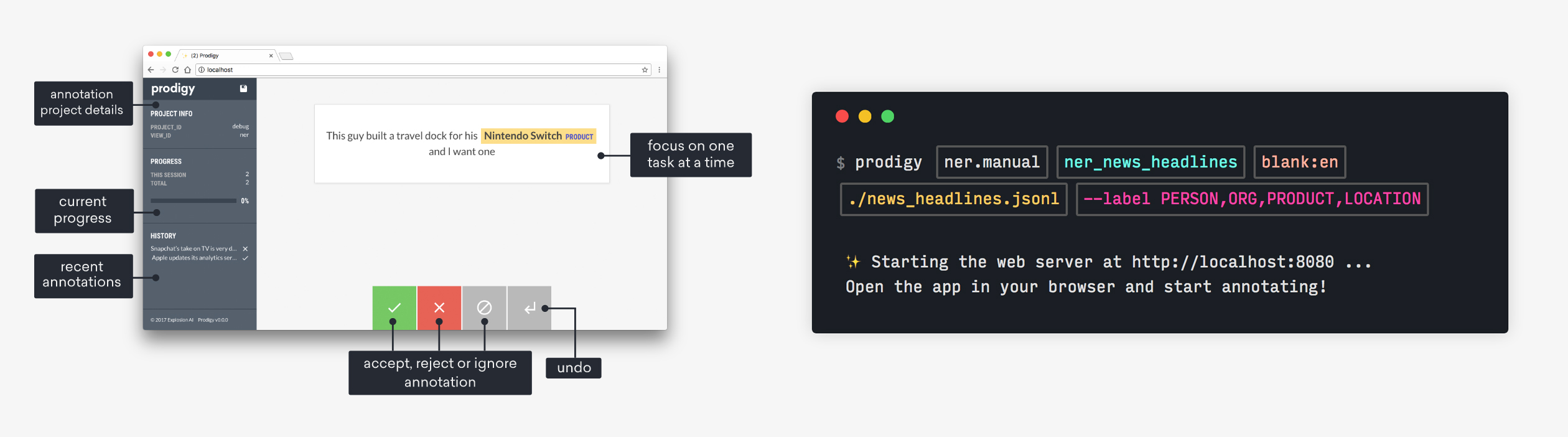
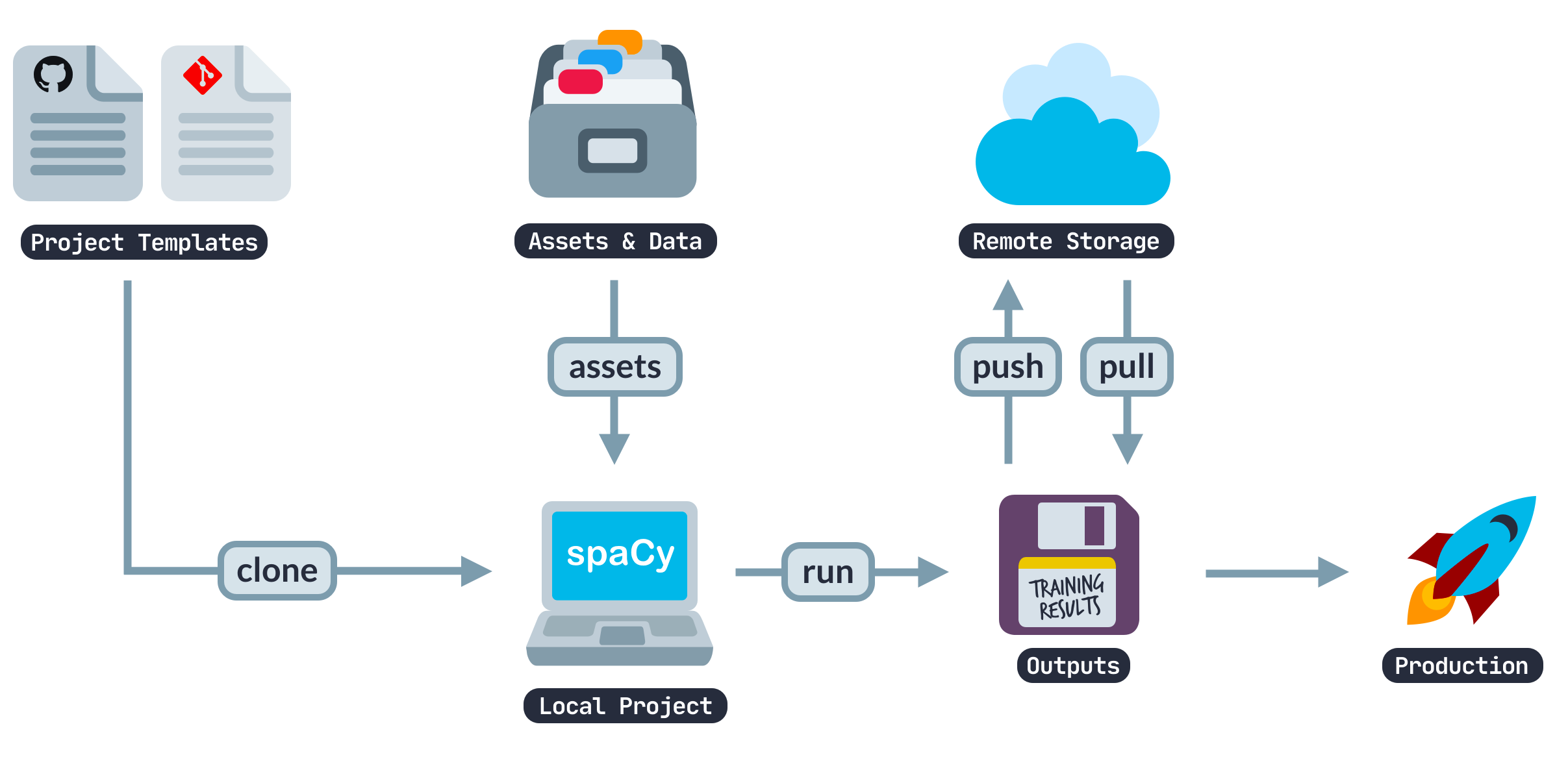
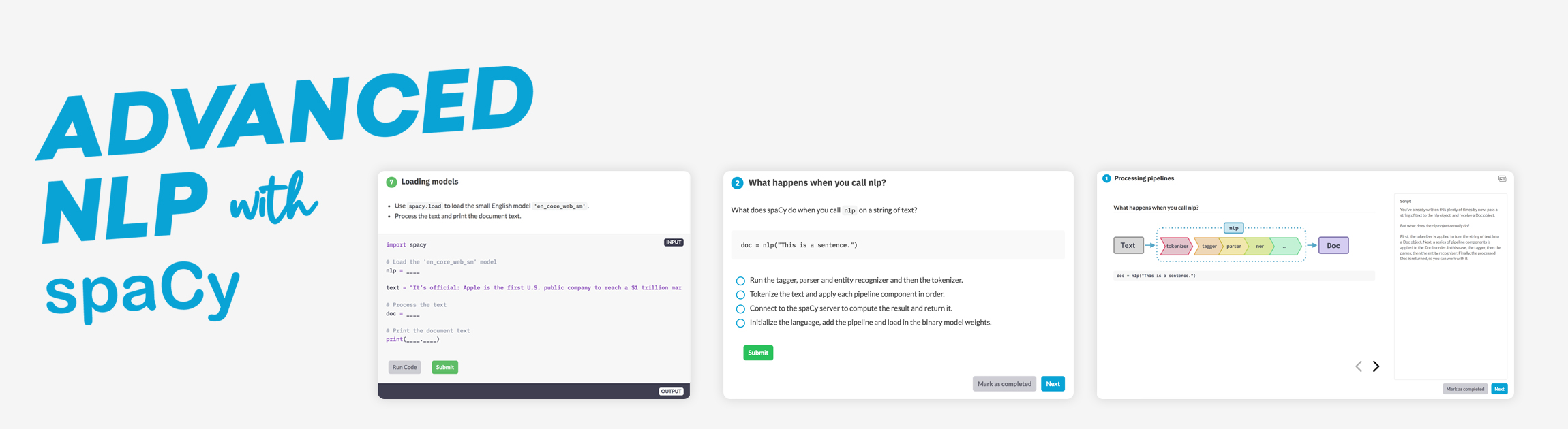
Get things done
spaCy is designed to help you do real work — to build real products, or gather real insights. The library respects your time, and tries to avoid wasting it. It's easy to install, and its API is simple and productive.
Blazing fast
spaCy excels at large-scale information extraction tasks. It's written from the ground up in carefully memory-managed Cython. If your application needs to process entire web dumps, spaCy is the library you want to be using.
Awesome ecosystem
Since its release in 2015, spaCy has become an industry standard with a huge ecosystem. Choose from a variety of plugins, integrate with your machine learning stack and build custom components and workflows.